



Irradiation is the process where the fire a pulsed beam of electrons at the diamond , which then disturbs the electron of the diamond itself, causing them to be knocked and captured by other atoms the light absorbing structure of the gem is changed and as a result is their "color".
we use only low energy electone method of irradition which is the safest way to irradiate diamonds.
Irradiated diamonds are genuine natural diamonds that exhibit an intense color change such as blue, cognac, green, yellow or pink.
High Pressure High Temperature (HPHT) process to enhance diamonds, performed only on the highest quality natural diamonds with no inclusions and high clarity grades on those diamonds are high quality and have a special chemistry that allows for color change.
the process allow the natural trace elements within a diamond to relax and to display their natural color .by using highly advanced HPHT machine expose the diamonds to heightened heat and pressure resulting in the change of color of the diamond.

A diamond's color grade actually refers to the absence of color. In other words, diamonds that are white, containing little or no color, receive higher quality grades than those with noticeable color.
A chemically pure and structurally perfect diamond has no hue, like a drop of pure water, and consequently, a higher value.
A color scale established by the Gemological Institute of America (GIA) assigns a letter to the degree of colorlessness found in a diamond. Beginning with D and ending with Z, each descending letter denotes an increasing amount of light yellow, brown or gray in the diamonds.
Color of the polished diamonds starts from Colorless D-F), near colorless (G-J), faint color (K-M), very light color (N-R), light color (S-Z) to fancy color (Z+). In diamond trade terminology is referred in alphabet starts from D to Z.
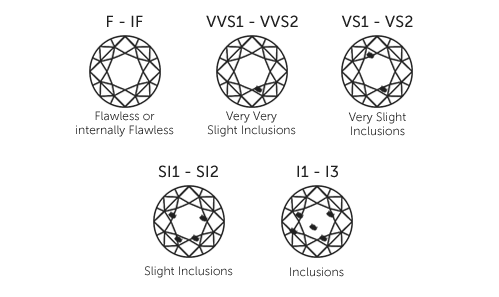
A diamond’s clarity is measured by the existence, or absence, of visible flaws. Tiny surface blemishes or internal inclusions — even those seen only under magnification with a jeweler’s loupe — can alter the brilliance of the diamond and, thus, effect its value.
FL, IF:Flawless, Internally Flawless. There are no inclusions — internal flaws — or blemishes — external flaws.
VVS1, VVS2: Very, Very Slight Inclusions. Hard to view such inclusions under 10x magnification. An excellent quality diamond.
SI1, SI2: Slight Inclusions. Inclusions are visible under 10x magnification and may not be visible to the naked eye when the stone is in the face-up position.
I1, I2, I3: Included: Inclusions are obvious under 10x magnification and may affect transparency and brilliance. I1 diamonds have inclusions that are almost always visible to the naked eye.
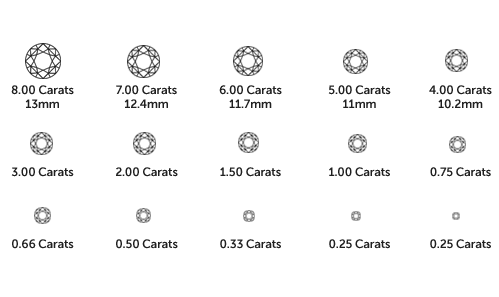
Diamond carat weight is the measurement of how much a diamond weighs. A metric "carat" is defined as 200 milligrams. Each carat can be subdivided into 100 'points.' This allows very precise measurements to the hundredth decimal place.
Carat reflects the weight of the stone, which includes depth, height and diameter of the stones. Prior to the twentieth century, diamonds were measured using carob seeds, which were small and uniform and served as a perfect counter weight to the diamond. The word "carob” is the origin of the word "carat" that we use today.
One carat is the equivalent of 0.2 grams One carat is also divided into 100 points. Points are generally used to describe increments of weight within a carat. The weight of a 3/4-carat diamond can be shown as .75 carats or 75 points.
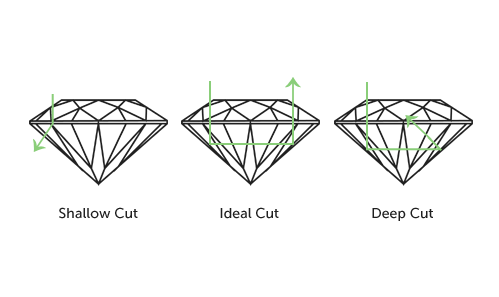
A diamond's CUT not only refers to its shape, but also how effectively the stone can return light back to the viewer's eye. A well-cut diamond will appear very brilliant and fiery, while a poorly cut stone can appear dark and lifeless. CUT verification can be done through comparison of parameters of facets. A well cut diamond will be symmetrically round, proper depth and width, and have uniformity of the facets.
A diamond cutter will follow precise mathematical proportions relating to the height, width and depth of the crown (top), girdle (widest part) and pavilion (bottom). When a diamond is cut to the right proportions, light reflects from one facet to another and then disperses through the top of the stone, resulting in a burst of fire and brilliance. Fire is the flashes of color one sees when you look at a diamond; brilliance is its sparkle.
Polish is the overall condition of the surfaces of a finished diamond. Polish is rated Good (GD), Very Good (VG), Excellent (EX), and Ideal (ID).
Symmetry refers to the precision of the shape and arrangement of facets in a diamond. Although to the naked eye finish features only have a tiny effect on appearance, symmetry is an significant aspect.